Measuring voltage is quite easy using any microcontroller as compared to the measurement of current. Measuring voltages becomes necessary if you are working with batteries or you want to make your own adjustable power supply. Though this method applies to any uC but in this tutorial, we will learn how to measure voltage using Arduino.
There are voltage sensors available in the market. But do you really need them? Let's find out!
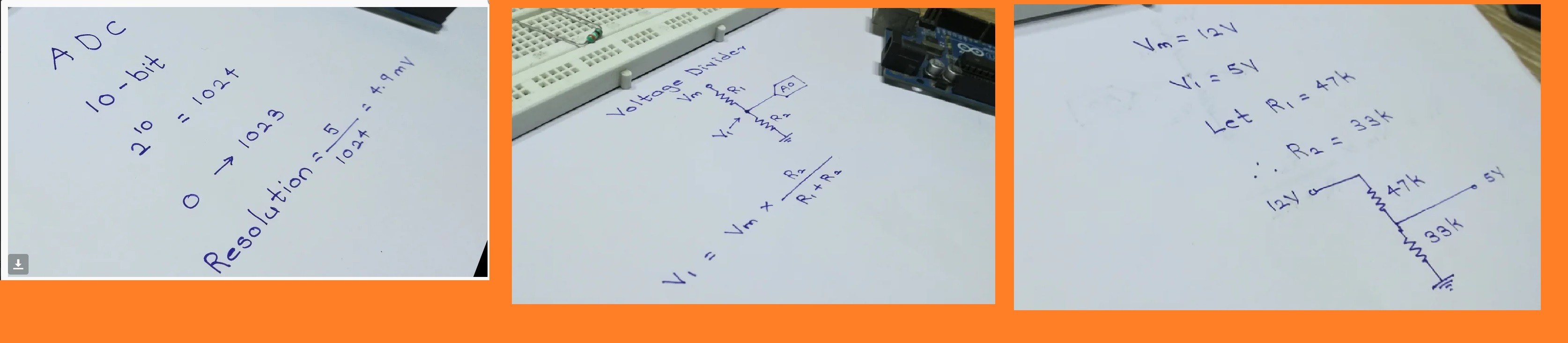
A microcontroller cannot understand analog voltage directly. That is why we have to use an Analog to Digital Converter or ADC in short. Atmega328 which is the brain of the Arduino Uno has 6 channel (marked as A0 to A5), 10-bit ADC. This means that it will map input voltages from 0 to 5V into integer values from 0 to (2^10-1) i.e. equal to 1023 which gives a resolution of 4.9mV per unit. 0 will correspond to 0V, 1 to 4.9mv, 2 to 9.8mV and so on till 1023.
But the problem arises when the voltage to be measured exceeds 5 volts. This can be solved using a voltage divider circuit which consists of 2 resistors connected in series as shown. One end of this series connection is connected to the voltage to be measured (Vm) and the other end to the ground. A voltage (V1) proportional to the measured voltage will appear at the junction of two resistors. This junction can then be connected to the analog pin of the Arduino. The voltage can be found out using this formula.
V1 = Vm * (R2/(R1+R2))
The voltage V1 is then measured by the Arduino.
Now to build this voltage divider, we first need to find out the values of resistors. Follow these steps to calculate the value of resistors.
- Determine the maximum voltage which is to be measured.
- Decide a suitable and standard value for R1 in kilo-ohm range.
- Using formula, calculate R2.
- If the value of R2 is not (or close to) a standard value, change R1 and repeat the above steps.
- Since Arduino can handle a maximum of 5V, V1 = 5V.
For example, Let the maximum voltage (Vm) to be measured be 12V and R1 = 47 kilo-ohms. Then using the formula R2 comes out to be equal to 33k.
Now, Build a voltage divider circuit using these resistors.
With this setup, we now have an upper and lower limit. For Vm = 12V we get V1 = 5V and for Vm = 0V we get V1 = 0V. That is, for 0 to 12V at Vm, there will be a proportional voltage from 0 to 5V at V1 which can then be fed into the Arduino as before.
Voltage Measurement Using Arduino
- Product Code: Learning only
- Availability: 2-3 Days
-
Rs0.00

